This example shows how to detect internal and surface cracks of a ceramic plate and make OK/NG judgment by using frequency analysis.
Place the sample ceramic plate on a soft sponge to make the position similar to the free vibration environment and hit with the impulse hammer. Capture the hammering sound and the excitation signal with the microphone. To process the frequency analysis, input the excitation signal and generated sound signal to an FFT analyzer and standardized the generated sound signal with excitation signal.
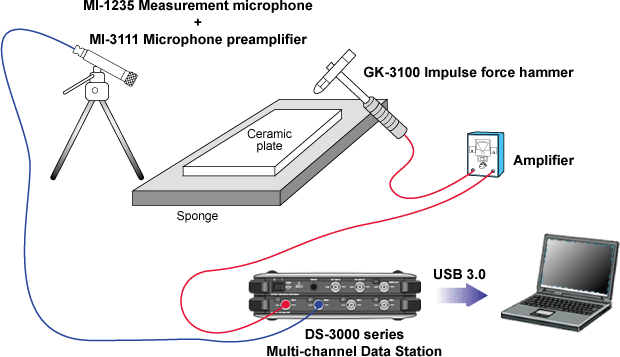
Configuration
| Model | Product name | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DS-3000 series | Multi-channel data station | ♦
DS-3204 4ch Main unit ♦ DS-0321 FFT Analysis function ♦ DS-0350 Recording function ♦ USB 3.0 Cable (2 m) |
| 2 | MI-1235 | Measurement microphone | |
| 3 | MI-3111 | Microphone preamplifier | |
| 4 | GK-3100 | Impulse force hammer | Including amplifier |
| 5 | DS-0321 | FFT Analysis software | 4 to 8 ch |
Measurement procedure
| 1. | The ceramic plate specimen is placed on a thick and soft sponge or suspended in the air so that the specimen will be free vibration as much as possible. |
| 2. | Hit the specimen with the impulse force hammer and measure the excitation waveform by the DS-3000 series. |
| 3. | Measure the hammering sound by the microphone. |
| 4. | Input the signals to the DS-3000 series and measure frequency response function by excitation waveform and response waveform. |
Analysis data example
As an important factor of hammering a ceramic plate, a soft sponge with 15-mm thickness is used so that the specimen will be free vibration.
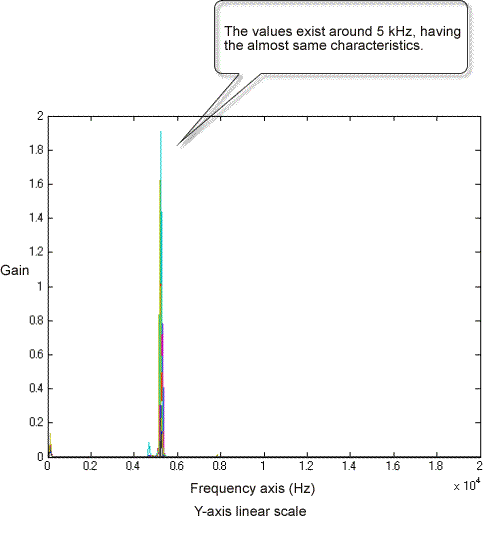
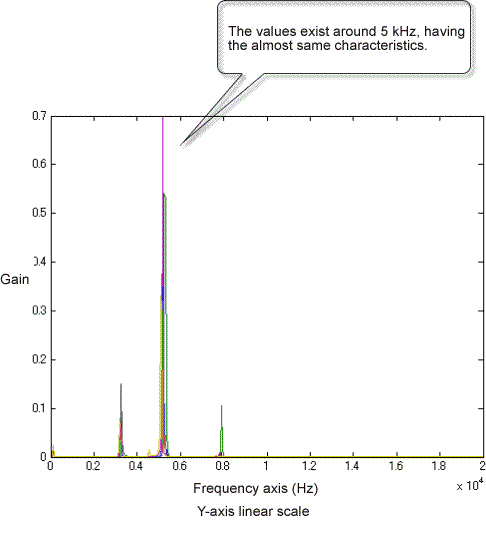
First, perform FFT analysis of hammering sound from a normal ceramic plate. In this example, center and edge point of the ceramic plate are excited by the hammer. As shown as the following, the peak values of the frequency response function exist on around 5 kHz (5.3 kHz).
Central excitation
Edge-point excitation
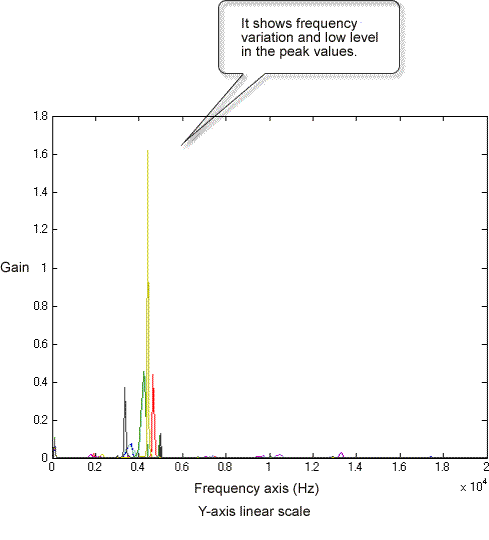
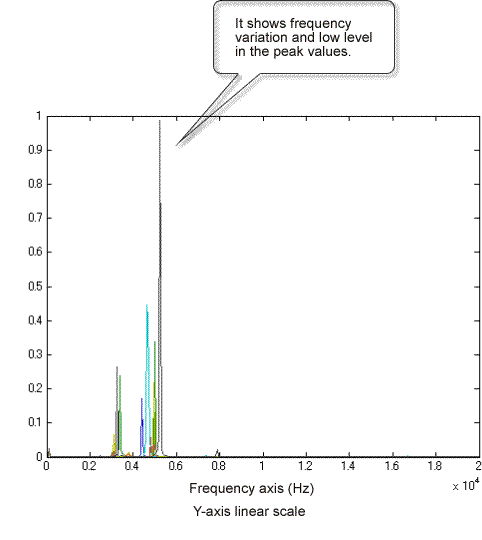
Next, perform FFT analysis of hammering sound from an NG ceramic plate. The hammering sound of an NG product has variation in the peak values of the frequency response function on the frequency axis compared to that of an OK product, and the peak values themselves are in lower level. The same results are obtained in the center and the edge excitations. From this result, this product has a certain defect on the surface or inside and is considered to have low rigidity for this reason.
Central excitation
Edge-point excitation
Usually, the hammering sound of a specimen having internal defect makes dull sound, which means the peak value of the natural frequency is heavily damped. However in most cases, it is difficult to quantify that damping on the auditory sensitivity.
Other measurement examples
• OK/NG judgment of a brake disc
• Judgment of crack in a ceramic material
• Detection of an internal crack in other homogenous materials
Measurement point
When you perform excitation, a measurement object should be set up to be free vibration. The frequency in the rigid body mode is expected to be one-tenth of its 1st order.
- The measurement object is suspended in the air to be free vibration.
- Place the measurement object on a soft material such as a sponge when the above
condition is difficult to set.
As the vibration of the measurement object having internal crack varies depending on the input force, the hammering force should be a constant.
Set up condition not to give influence of nonlinear factors which are not related to the measurement (clatter, friction).
It is difficult to make OK/NG judgment, when the frequency characteristics of a product are not stable due to the remained nonlinear factors etc.
Revised:2011/11/02
