
What is the principle of the insulator thickness measurement of the CL-5610 Non-contact Thickness Meter?

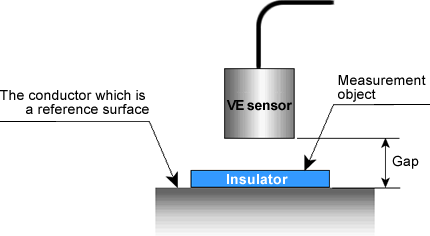
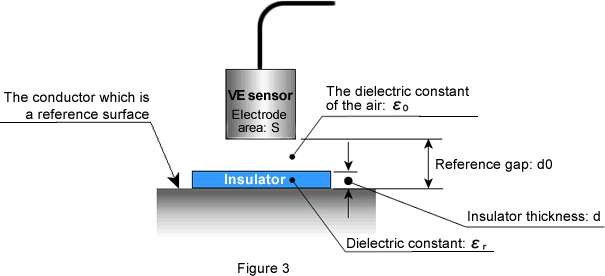
To enable the insulator thickness measurement with the CL-5610 Non-contact Thickness Meter, fix the VE sensor and the reference surface, and insert the insulator to be measured in between as shown in the following figure.
Operation procedure
1. Set the VE sensor to the reference surface of the conductor within the range of specified sensor gap.
2. Measure the gap between the VE sensor and reference surface.
3. Setup the dielectric constant of the insulator to be measured to the CL-5160.
4. Insert the measurement insulator into the reference surface without changing the reference gap.
Why this procedure enables to measure the thickness of the insulator?
To make the insulator thickness measurement using the CL-5610 more understandable, think about how to calculate the electrostatic capacitance when the different dielectric constant object is inserted to a part of condenser.
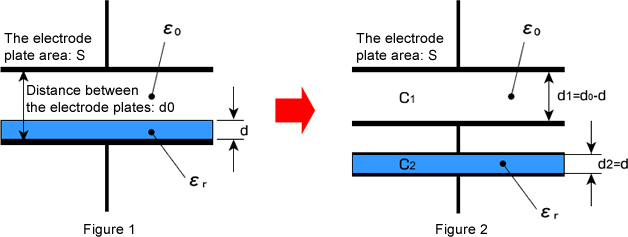
First of all, think about the condenser as shown in figure 1.
Gap between the electrode plates: d0, electrode area: S, dielectric constant: ε0 (air), dielectric constant of the inserted insulator: εr and thickness: d
The electrostatic capacitance (C) of this condenser is the synthetic capacity when connecting the condenser between [the condenser of the gap between plates (d0 - d) and dielectric constant (ε0) (capacitance is C1)] and [the condenser of the gap between plates (d) and dielectric constant (εr) (capacitance is C2)] in series. (Figure 2)
When the condensers are connected in series, the relation of the synthetic capacity (C) and each capacity of (C1) and (C2) can be established in following formula.
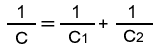
In this condition, you can calculate as;
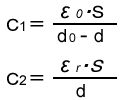
The synthetic capacity (C) which consists of (C1) and (C2) is as follows.
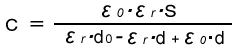
The relation formula of above synthetic capacity is;
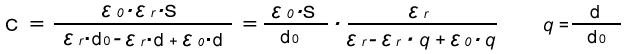
In above figure, ε0 and S values are known, d0 can be calculated before inserting the insulator. The electrostatic capacitance C can be calculated when the insulator is inserted. Therefore, if εr of the insulator is known, the thickness d can be obtained.
However, εr is unknown in many cases, so the thickness d can be obtained by the following procedure.
1. Obtain d0 by calculating the electrostatic capacitance which has nothing in between.
Revised:2013/08/08