No. 4 Torque measurement instrument: Why we measure torque?
In the previous columns, we have introduced "Why measure sound and vibration" and "Sound measurement instrument".
In this column, I would like to talk about "why we measure torque?" and "torque measurement instrument".
What is torque?
It represents a force to rotate around the axis.
For example, when riding a bicycle, you have to pedal, and the force of pedaling is equivalent to torque. In addition, when opening and closing a door, the force of turning a door knob, and when opening and closing a cap of a PET bottle, the force of applying to the cap.
The unit of torque is written as N·m in the international standard and is read as "Newton meter".
Why we measure torque?
I explained that torque is "the force to rotate".
In the case of the bicycle earlier, great torque means that the pedaling force is strong, and the stronger the pedaling, the faster the bicycle will accelerate. In other words, “great torque = great acceleration”.
The great acceleration means that the number of wheels rotating (rotational speed) increases within a certain period of time. Thus, the bicycle speed is faster and it is possible to travel a longer distance.
The bicycle mentioned above is just one example, and rotating machinery and parts are used in many fields, both industrial and consumer. Torque measurement is one of the important indicators to evaluate their performance.
Torque sensors (detectors)
There are two methods for detecting torque: phase difference method measuring torque from the torsional angle (phase angle) of the shaft and strain gauge method measuring torque from the torsional strain of the shaft, which have two types.
- Phase difference method
- 1) Using electromagnetic gears type
- 2) Using electromagnetic induction theory type
- Strain gauge detection method
- 3) Strain type
- 4) Magneto‐striction type
Our torque detectors adapt the detection method 1), 2), and 3).
In this column, I will explain 1) and 2), which have many sales records.
Principle of torque detector
(1) Phase difference method using electromagnetic gears
As shown in Fig. 1, the torque detector has gear A on the drive side and gear B on the load side of the torque transmission shaft. The torsion angle between gears A and B is measured as the phase difference. The movement of each gear is detected by the electromagnetic detectors C and D, the output signals are input to the torque meter, and the torque value is calculated from the phase difference of the signals. Torque is generated not only when the axis of the object is rotating, but also when it remains stationary. In this detection method, the rotating hollow cylinder is constantly rotated at a constant rotation speed by the detector’s motor. Therefore, phase difference of signals are always generated, and torque is detected even if the axis of the object is stationary.
Fig. 1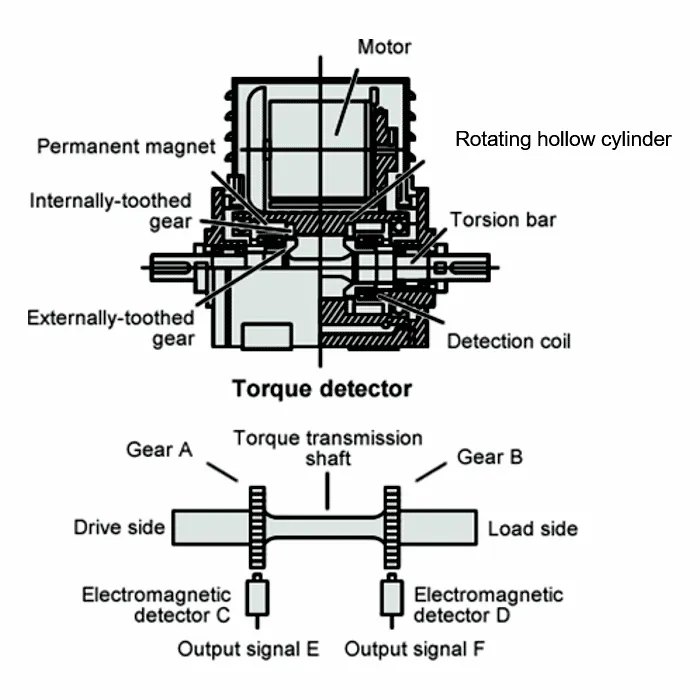
(2) Phase difference method using electromagnetic induction theory
As shown in Fig. 2, phase difference plates are installed on the drive side and load side of the torque transmission shaft, and the drive coil and the detection coil are arranged to sandwich the plates respectively. When the torque shaft is rotated, the magnetic flux transmitting through the phase difference plate changes.
The magnetic signal is converted into voltage signals by the two detection coils and the torque meter calculates the torque value from the phase differences.
Fig. 2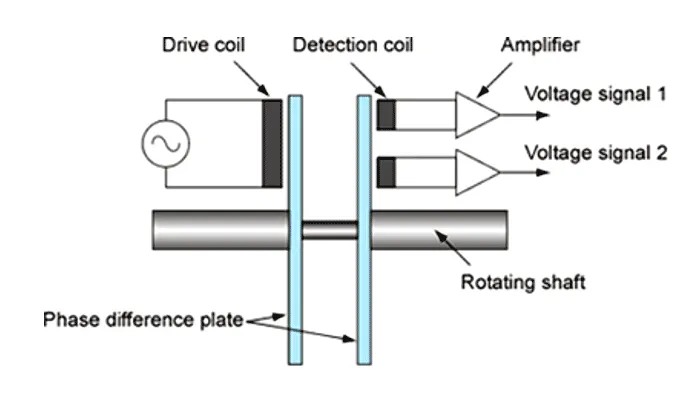
This time, I briefly talked about torque measurement. It is necessary to select the optimum torque detector that suits the purpose and application as it has characteristics depending on the detection method.
I would like to talk about these at another time.
(AM)
[Torque & Related products]
https://www.onosokki.co.jp/English/hp_e/products/category/torque.html
