- HOME
- Ono Sokki's Patio
- Sound diffraction

Sound diffraction
Ken: We came back from Disneyland yesterday driving on high way. There were walls on both sides of some roads. Are they for noise reduction, aren’t they?
Dad: Yes, they are. Precisely, we drove on Metropolitan Expressway yesterday. There were some places where they built noise barrier on side of roads to avoid traffic noise from disturbing tenants and dwellers in buildings and houses nearby.
Ken: How effective are the noise barriers?
Dad: It is a very difficult question. Let me explain it in order. Though building a noise barrier, you can not vanish noise in complete, can’t you? Once you build it, cars are out of sight but you still hear their noise at a lower amount of level. This kind of phenomenon with sound coming around from behind is called “Sound diffraction”. A light will not come around if there are obstacles on ahead but a sound will.
Ken: It seems same as a light makes a shade when light of sun or dim bulb is blocked. But why does sound come around from behind while light doesn’t?
Dad:It is the point. You know that both light and sound are wave. The wavelength of light is 1/1million of sound. The wavelength of light is shorter than 1/1000 of 1mm and this is much shorter than anything around you. So when it is blocked by something, the backside of it becomes a shade. There may be no shade if a hair blocks light.
Ken: Then, sound has 1 meter of wavelength as it is 1million
times of 1/1000 or 1000 mm. 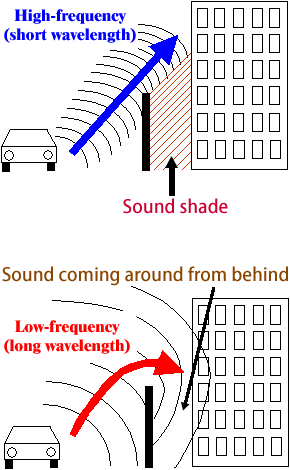
Dad: A frequency of a sound with 1-meter-wavelength is about 300 Hz which is equal to an average frequency of a woman’s voice. Each wavelength of sound or light human being can sense has a breadth respectively. I said that light is shorter than 1/1000 of 1mm. To be precise, optical wavelength is between 0.4 and 0.8 µ m and colors of rainbow from red to violet are those in between. Frequency of sensible sound is from 20Hz to 20 kHz and this is from 17mm to 17m in terms of wavelength. Sound travels approx.340 meters per second. Vibrating once per second is 1Hz. So the wavelength of 1Hz sound is 340 meters, the one of 10Hz is 34 meters and the one of 10 kHz is 34mm.
Ken: I see. The wavelength of sound is so long that it comes around from behind.
Dad: Right. Basically sound has longer wavelength than light. Shorter wavelengths or high frequency wavelengths range from a few centimeters to a dozens of centimeters at most. The sound does not come over sound barriers with dozens of meters wide because the backside of the barrier is a kind of shade as in the case of light.
Ken: I got it. On the contrary, a sound of low frequency is a few meters wide. This is wider than barrier height and it gets over and come around from behind, doesn’t it?
Dad: You’ve got that right. Though you build a noise barrier, it diminishes rasping sound only a bit. It does not work for low-pitched sound. However, noise by vehicles has a frequency characteristic whose highest point is around 2kHz and this is a frequency human ear is most sensitive to. A noise barrier is effective to sound with such a frequency, so it is widely used for highways etc. built close to buildings and houses which require abating loud noise. In designing a noise barrier, we measure frequency characteristics of noise on site and consider effectiveness of the barrier at a point of receiving noise. The design of a barrier needs to meet the environment standard, or a noise regulation established by the government which controls noise level at a receiving point.
- © ONO SOKKI CO., LTD. 1996-2026
